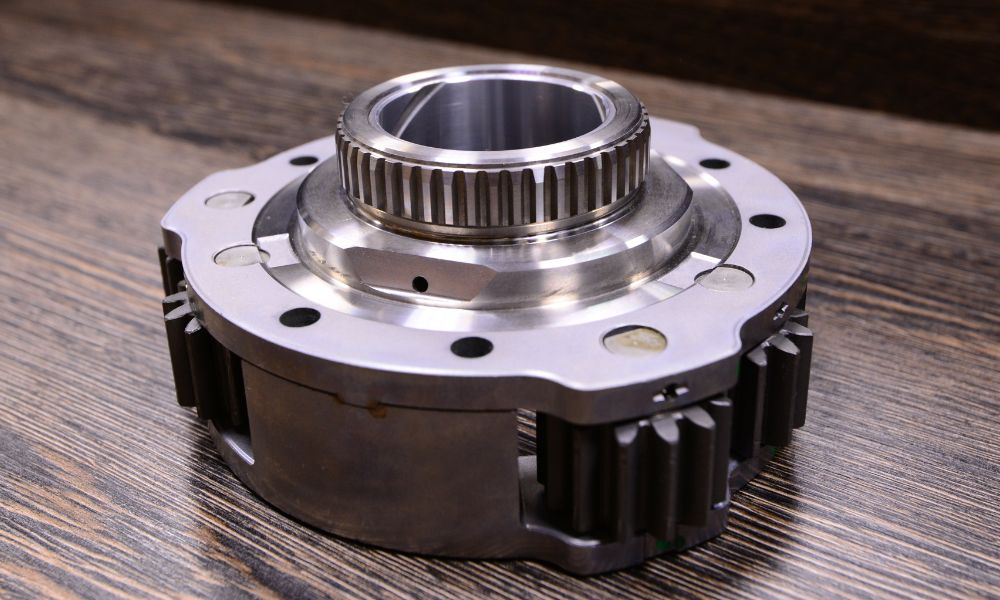
The transfer case is a key component that enables the distribution of power to all four wheels in four-wheel drive (4WD) and all-wheel drive (AWD) vehicles. This device is responsible for managing and transferring the power from the vehicle's transmission to the front and rear axles. Continue reading to learn how the transfer case works in 4WD and AWD vehicles.
How 4WD Transfer Cases Function
Four-wheel drive vehicles are special because they are compatible with two types of transfer cases:
Part-Time 4WD Transfer Cases
Part-time four-wheel drive vehicles rely on the transfer case. The manual control feature allows drivers to switch between two-wheel drive and 4WD modes. In 2WD mode, power goes solely to the rear axle. However, engaging the 4WD mode activates the transfer case and sends power to the front and read axles. This balanced torque allocation strengthens traction and control.
Transitioning from 2WD to 4WD is seamless, but the driver should switch modes based on the driving conditions. Consistent use of 4WD mode on average pavement can accelerate the depletion of the drivetrain.
Part-time 4WD transfer cases offer the best of both worlds. They provide the flexibility of 2WD for everyday driving while delivering incredible control when the situation demands it.
Full-Time 4WD Transfer Cases
The full-time four-wheel drive vehicles maintain an ongoing power supply to all four wheels. The continuous engagement improves handling and traction when navigating demanding terrains.
The transfer case splits the engine's torque between the front and rear axles. Typically, it operates in a 50:50 ratio, but this can vary based on the vehicle's design or the road conditions. The key feature of full-time 4WD transfer cases is the addition of a differential. It allows the front and rear axles to turn at different speeds.
How AWD Transfer Cases Function
You might think that full-time 4WD and AWD operate in a similar fashion. While the two are incredibly similar, they are not the same.
AWD systems feature transfer cases that are always engaged, distributing torque between the front and rear axles. However, the distribution is not always balanced; it varies depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
AWD transfer cases work in conjunction with the vehicle's electronic control unit (ECU) to monitor wheel speed, throttle position, and steering angle. When the ECU detects a difference in wheel speeds, it sends a signal to the transfer case. In response, the transfer case adjusts the power distribution, directing more torque to the axle with better traction. Dynamic shifting maintains control of the vehicle, which is especially important on slippery or uneven terrains. This increases the safety of the transmission’s operation and the entire vehicle.
Understanding how transfer cases work in 4WD and AWD vehicles is as valuable as maintaining the transfer case parts. That’s why Transparts Warehouse offers superior aftermarket automotive products to guarantee your transmission functions safely and smoothly. Find out your car’s make and model to select the exact products you need.