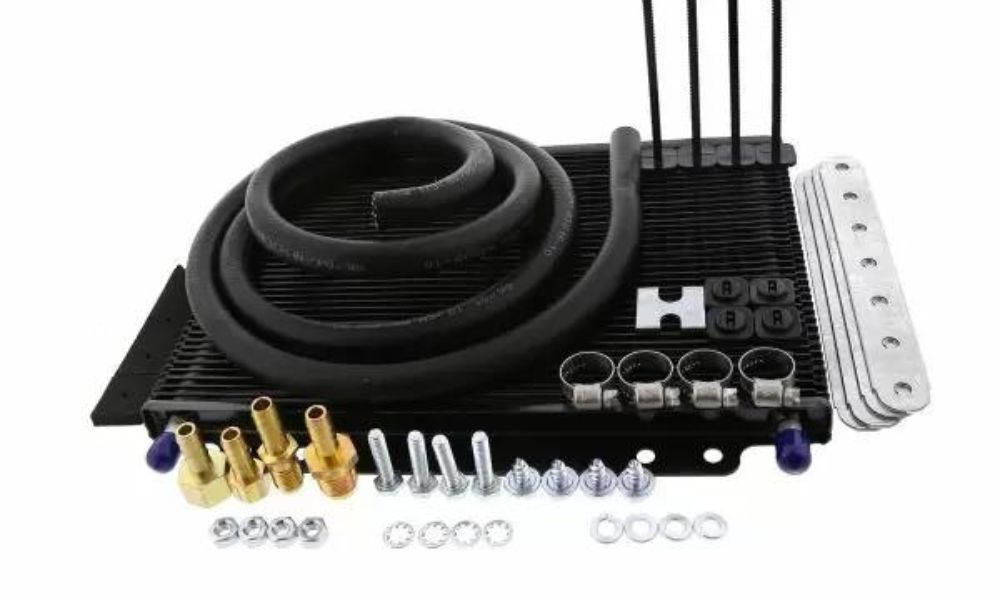
With so many mechanical and electrical components, understanding the inner workings of cars can be confusing. You need more information so that you can properly care for your vehicle. Let’s find the answers to the most frequently asked questions about transmission coolers and get to the bottom of this automotive mystery.
Do Both Manual and Automatic Cars Need Transmission Coolers?
Automatic cars generate more heat due to their complex operational design. In these vehicles, the automatic transmission fluid (ATF) lubricates and acts as a coolant, reducing the high temperatures produced.
However, under heavy loads, such as towing, uphill driving, or in high-temperature environments, the ATF’s cooling capacity may not suffice. This is where transmission coolers come into play. They protect the automatic transmission from overheating to prolong its longevity.
Manual cars typically do not utilize transmission coolers. They do not generate as much heat as automatic transmissions do, making cooling systems such as transmission coolers unnecessary. The primary source of heat in an automatic transmission is the torque converter, which is absent in manual transmissions.
However, it’s worth noting that there are exceptions, particularly in heavy-duty applications where manual transmissions and differentials might need cooling. In such cases, a pump would be necessary to facilitate the use of a transmission cooler with a manual transmission. Nonetheless, these scenarios are not the norm, and very few auto manufacturers opt to use transmission coolers for their manual transmissions.
What Is the Safe Temperature Range of Transmission Fluid?
Transmission fluid operates safely between 175 and 225 degrees Fahrenheit. The optimal operating temperature is around 200 degrees. Within the range, the fluid can effectively lubricate the moving parts and maintain the transmission’s overall health.
It’s important to note that if ATF fluid reaches 240 degrees Fahrenheit and above, the transmission is in grave danger. That’s why a transmission cooler is an essential tool to regulate temperature and protect the vehicle.
Where Are Transmission Coolers Installed?
It’s essential to position the cooler in a position for unobstructed airflow. Typically, mechanics achieve optimal airflow by securely attaching it to the front of the radiator or A/C condenser. As a result, the cooler can efficiently draw in cool air to reduce the ATF temperature.
What Are the Different Styles of Trans Oil Coolers?
There are three different styles of trans oil coolers. The various designs give buyers options to optimize the cooling performance based on their vehicle.
Tube and Fin
Tube and fin transmission coolers have a simple yet efficient design. They function with fluid circulating through a tube while the fins absorb and disperse heat.
This design relies on the natural flow of surrounding air to operate. While this approach typically suffices in regular circumstances, it may not provide adequate cooling in more demanding scenarios.
Plate and Fin
The fluid cooling system operates by channeling the fluid through cooling plates. The strategically positioned fins then absorb the heat.
The expanded surface area of the plates is an innovative design that offers exceptional efficiency. With improved heat transfer, the plate and fin trans oil cooler design offers superior cooling performance.
Stacked Plate
Among the three designs, the stacked plate transmission cooler stands out as the most efficient. It boasts a configuration of multiple plates stacked together, resulting in a generous surface area that ensures optimal cooling. As the fluid courses through the plates, heat dissipation occurs swiftly, thanks to the sizeable surface area.
These coolers find their home in high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty trucks, as they can withstand high fluid pressures and deliver unparalleled cooling capabilities. Nevertheless, they also come with a higher price tag compared to the other two styles.
What Does the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) Mean?
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) refers to the maximum operational weight of a vehicle, as specified by the manufacturer. This rating includes the weight of the vehicle itself, passengers, cargo, and any additional equipment installed.
Understanding the GVWR is particularly important when selecting a suitable transmission cooler. A vehicle functioning close to its GVWR is likely to generate more heat, thereby increasing the demand for effective cooling. For instance, a heavy-duty truck with frequent towing duties, operating close to its GVWR, would require an efficient cooling system—typically a stacked plate transmission cooler—to prevent transmission overheating.
What Metals Are Transmission Coolers Made From?
Aluminum is the most used metal for transmission coolers. Nevertheless, both aluminum and steel are popular options.
Aluminum Transmission Coolers
Aluminum transmission coolers are popular due to their lightweight properties and excellent thermal conductivity. The high thermal conductivity of aluminum allows for efficient heat dissipation, making it an ideal material.
It’s also important to mention that aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion. The transmission cooler is wonderfully durable and won’t wear down from a little pressure.
Steel Transmission Coolers
Steel is much heavier than aluminum, and its robust nature withstands extreme conditions. However, steel has a lower thermal conductivity.
It may function less efficiently than aluminum. That’s why steel transmission coolers have a much larger surface area to combat the reduced thermal conductivity.
What Is the Average Size of Transmission Coolers?
Transmission coolers come in a range of sizes to cater to different vehicle requirements and operating conditions. The cooler’s core dimensions (height, length, and thickness) determine the size of a transmission cooler. Typically, the average size of a transmission cooler is around 7.5 inches in height, 11 inches in length, and 0.75 inches in thickness.
However, these dimensions can vary widely based on the specific model and the intended use of the cooler. For instance, heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and RVs, often require larger coolers due to their high GVWR and the intense heat loads they generate. Conversely, smaller, lightweight vehicles typically necessitate more compact coolers.
Remember, the size of the cooler should correlate with the heat dissipation needs of the vehicle. Larger coolers have more surface area for heat to escape, thereby offering superior cooling capabilities. However, they can be more challenging to install due to their size and may not fit all vehicle models.
Smaller coolers, while easier to fit, may not provide adequate cooling for vehicles subject to high-stress conditions such as towing or racing. It’s crucial to ensure that the chosen cooler is a good fit for the vehicle’s specifications and usage conditions to ensure optimal transmission performance.
How Can You Find a Quality Transmission Cooler?
High-quality automatic transmission coolers aren’t difficult to find when you know where to shop. Transparts Warehouse is a trustworthy aftermarket transmission parts supplier that’s ready to assist! Whether you have an everyday driver or a truck designed for hauling cargo, we have a great selection of transmission coolers.
Finding answers to frequently asked questions about transmission coolers is often more difficult than you might think! But now, you should have the information you need to purchase the right transmission cooler for your vehicle to operate smoothly.