The technology of automobiles has come a long way since their invention in 1886. Singular gear speed vehicles rapidly evolved into multi-speed manual transmissions. Now, automatic transmission is used in nearly every car, truck, and SUV on the market.
But what makes automatic transmission so technologically advanced? And how does it work? Explore the world of electronics and software in automatic transmissions.
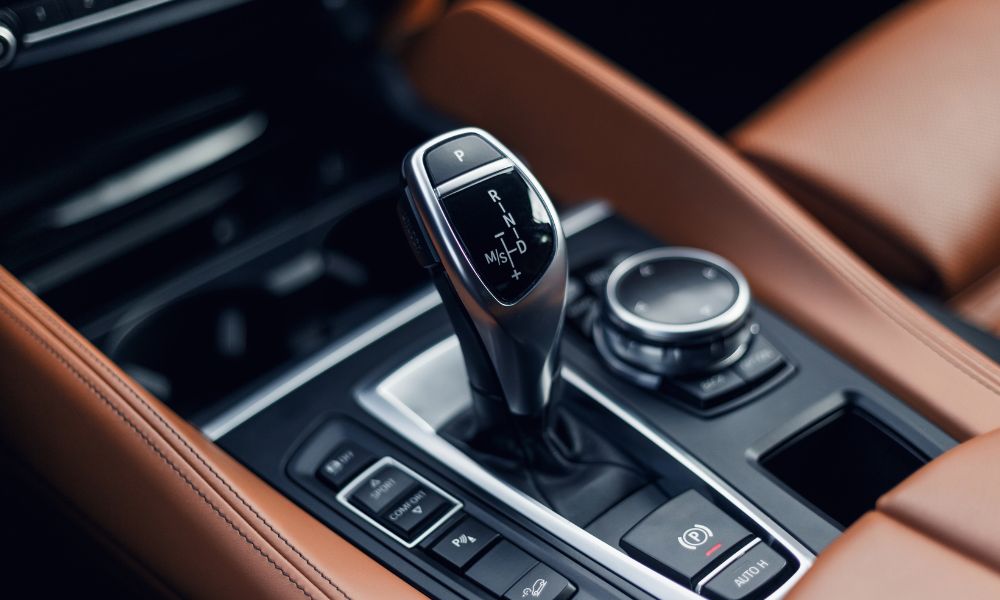
Electronic Control Units
Electronic control units (ECUs) are the brains behind modern automatic transmissions. These units monitor variables such as engine speed, throttle position, vehicle speed, and transmission oil temperature. They store maps of various ratios and decide the appropriate gear based on driving conditions and the driver’s input.
Modern ECUs are highly sophisticated. With the ECU in place in a vehicle, each driver can enjoy a smoother, more responsive ride. The ECU ensures that the automatic transmission shifts gears at the proper time to enhance fuel efficiency.
The ECU receives data from various sensors located throughout the vehicle. These sensors monitor elements such as vehicle speed, throttle position, brake status, and more. Based on the data received, the ECU makes decisions about the operation of the automatic transmission.
For instance, when you press the accelerator pedal, the throttle position sensor sends a signal to the ECU indicating the degree to which the pedal is depressed. The ECU interprets this signal and decides when and how to shift gears to provide the best possible balance between speed and fuel efficiency.
Moreover, the ECU in an automatic transmission allows for advanced features like adaptive driving modes. For example, some cars offer Sport or Eco modes that change the transmission’s behavior to prioritize performance or fuel efficiency, respectively. The ECU enables these features by adjusting the transmission’s operation based on the selected mode.
The Sensors That Impact the ECU
There are sensors installed all around a vehicle to transmit reliable data to the ECU and transmission software. With each sensor accumulating information, they provide the ECU with the necessary data to control the automatic transmission’s functions.
To gain a better understanding of the effort your vehicle puts in every time you drive, there are three types of sensors you should know about in automatic transmissions.
Transmission Speed Sensor
The transmission speed sensor detects the input, output, or intermediate speed of the transmission. Then, it relays the information to the transmission control unit. From there, the ECU determines when to shift gears for optimized performance based on the transmission’s speed.
Gear Position Sensor
The gear shift lever position sensor is a crucial component in an automatic transmission. It detects whether the gear shift lever is in park (P), neutral (N), reverse (R), drive (D), or a specific gear. This information allows the ECU to apply the appropriate bands or clutches, ensuring the vehicle moves or stays stationary as intended.
Parking Lock Sensor
The parking lock sensor detects whether the parking pawl—a device that locks the transmission—is engaged or disengaged. When parking or leaving a vehicle, the driver shifts the transmission to the park mode. The sensor then sends a signal to the ECU confirming the engagement of the parking pawl. This way, the vehicle is safe from moving unintentionally while unattended, protected from transmission damage, and secure when positioned on an incline.
Automatic Transmission Software
You now have a better understanding regarding the role of the ECU and how the sensors support vehicle operations, but how does the ECU interpret the information? Explore the electronics of automatic transmission further by learning more about its software.
Automotive engineers embed different types of software into vehicles to control every aspect, from steering to speed. The electronic control unit utilizes one form of software popularly used in automatic vehicles today.
Without this type of software, the vehicle will struggle to uphold its performance. This technology plays a crucial role in making driving accessible.
Vehicle Telematics: A Popular Form of Commercial Vehicle Software
Of course, other forms of software are used besides the ECU. Telematics is another system that utilizes a tracking device.
This device communicates with the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) system and uses GPS technology to collect and transmit data. Telematics also involves wireless safety communications and emergency warning systems. Just like other software systems, Telematics permits the sending, receiving, and storing of data.
Telematics is a popular type of software used for commercial purposes. The information gathered from the vehicle is transmitted to a server through a wireless network. This design is beneficial for schools, government officials, and commercial drivers that require regular updates regarding a particular vehicle’s whereabouts.
With Telematics, there’s more information being relayed than just the vehicle’s location; this software is now also utilized to learn about drivers’ habits. This tactic allows for the collection of data about a driver’s acceleration, braking, and speeds to promote safer driving.
The Crucial Role of Solenoids
There is one final component that supports the advanced system of automatic transmissions. Solenoids are electromagnetic devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They receive electric signals from the transmission control unit (TCU), which activates the solenoid to control the flow of fluid in the transmission.
Two Types of Solenoids
There are two primary types of solenoids used in automatic transmissions: shift solenoids and pressure control solenoids.
Shift solenoids control the engagement and disengagement of the gear sets in the transmission. When the TCU determines a gear change is necessary, it sends a signal to the appropriate shift solenoid. The solenoid then opens or closes a hydraulic valve to start or stop the flow of transmission fluid to the clutch pack. This action either engages or disengages the clutch pack, resulting in a gear shift.
Pressure control solenoids, on the other hand, regulate the hydraulic pressure within the transmission. The pressure within the transmission must be precisely controlled to ensure smooth gear shifts. Too much pressure can cause harsh shifting, while too little pressure can result in slippage between shifts. The TCU uses the pressure control solenoids to increase or decrease the transmission pressure as needed for optimal performance.
Automatic transmissions are intricate mechanisms that incorporate advanced electronics and software. Each technological element of automatic transmission is essential to promote a smooth, safe, and efficient drive.
When one transmission component falls out of line, you should know where to find trustworthy automatic transmission parts for sale. At Transparts Warehouse, you can shop for vehicles manufactured by GM, Honda, Ford, and more, and browse through our amazing selection of high-performance transmission parts. When you need your automatic transmission back in great condition quickly, our friendly team is here to help.